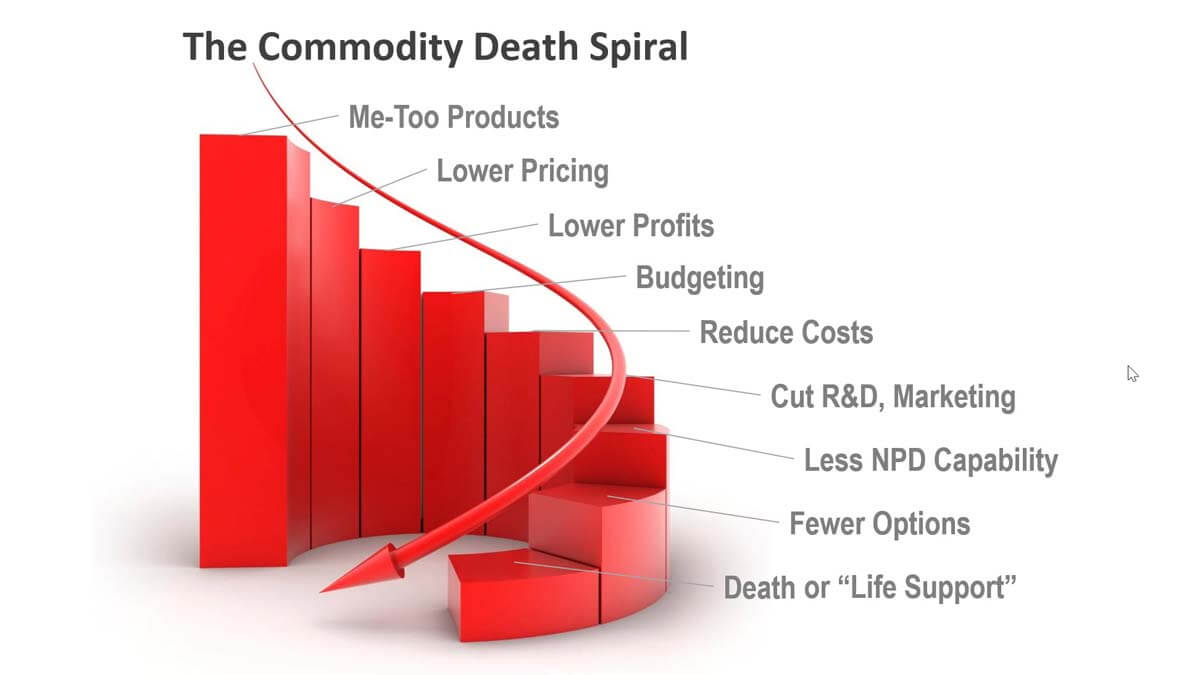
Here’s how the Commodity Death Spiral works: First, you stop innovating and offer me-too products that are interchangeable with competitors’. This lets purchasing agents demand lower pricing, which lowers your profits. Now it’s budgeting time and your boss wants higher—not lower—profits, so you must reduce costs. You cut R&D and marketing since you don’t need them this year. Of course, you’ll have even less new product development capability next year.
Eventually, you reach the point of no return, and your business dies… or goes on “life support” and is no longer relevant. Sadly, many businesses are on this downward spiral right now, and either don’t know it, or don’t want to admit it. They need a wake-up call, or the employees in that business will suffer.
More in this 2-minute video, Avoid the commodity death spiral
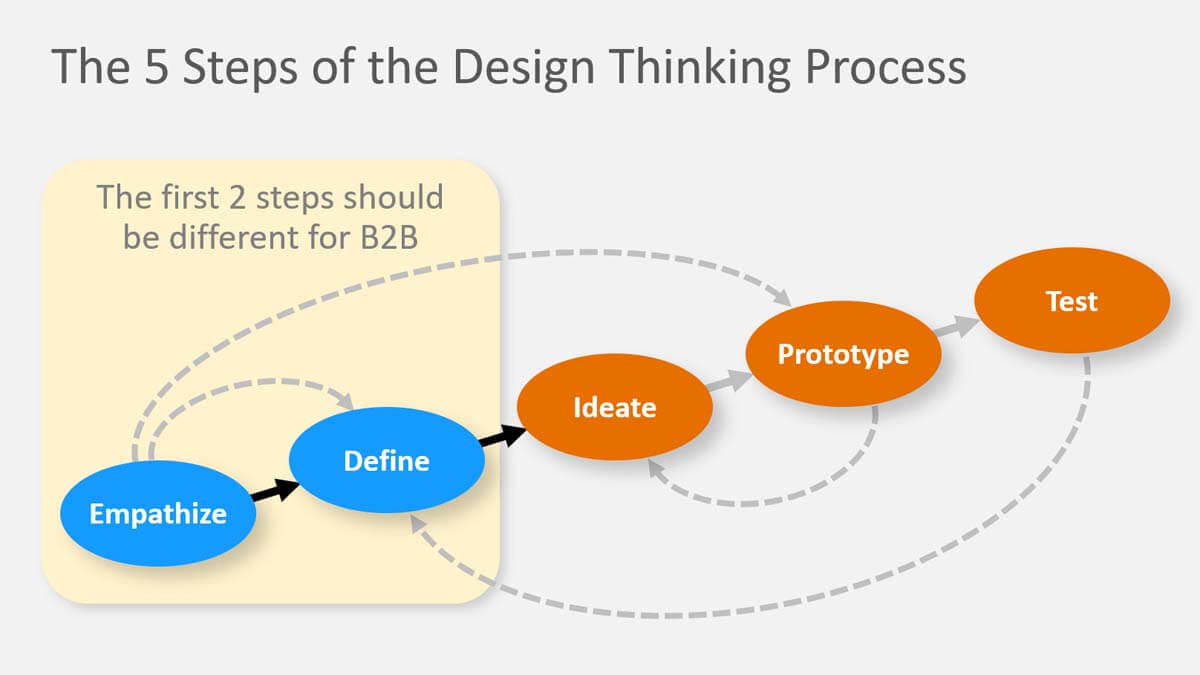
Design thinking is a powerful methodology for solving “wicked problems.” Unlike the well-stated problems we were given to solve in engineering school, these require figuring out what to work on, not just how to solve the problem. This perfectly describes real-world new product innovation, where we need to first understand customer needs.
As this diagram shows, the first two steps are “empathize” and “define.” Here’s the good news for B2B producers: You can do this much more effectively that B2C counterparts by using Discovery interviews (for “empathize”) and Preference interviews (for “define”). Check out this white paper to see why… and how: Design Thinking for B2B
In general, we do consider in-person interviews to be the gold standard. But there are 10 advantages of virtual VOC you shouldn’t overlook: 1) lower cost, 2) reaching dispersed customers, 3) viewable probing tips, 4) training for colleagues, 5) probing suggestions, 6) assistance for note-taker, 7) rapid de-briefing, 8) easier scheduling, 9) low-impact cancellations, and 10) greater project speed. To maximize effectiveness and efficiency, you’ll be wise to blend and balance both types of VOC. (See 2-minute video, Conduct virtual customer interviews.)
More in white paper, Virtual VOC
The “consumption job” may be the most important concept that you’ve never heard of. Consider this. We are all unique, or we think we are, with this problem: our products are becoming more and more like commodities. You know, gasoline, steel, topsoil. Our superior product dreams are trampled under the heavy feet of commoditization. Wouldn’t ... Read More
In 1965, DuPont scientist Stephanie Kwolek synthesized the first Kevlar polymer, an amazing fiber with five times the strength of steel. DuPont invested several hundred million dollars to commercialize the technology for tire cords, with disappointing results. It would be another decade before the company found its first major market for this material: bullet-proof vests.
How well does your company commercialize technology? Want to do it faster, more efficiently, and with greater confidence? You can, with six steps outlined in this white paper, Commercialize technology in 6 foolproof steps.
More in this 2-minute video, How to pursue transformational projects
Everyone wants to use metrics to monitor their innovation. That's fine… but unless you’re using “intermediate” metrics, you could be missing 3 qualities of a good metric: 1) predictive, 2) insightful, and 3) actionable. Consider these 12 intermediate metrics for your business. ... Read More
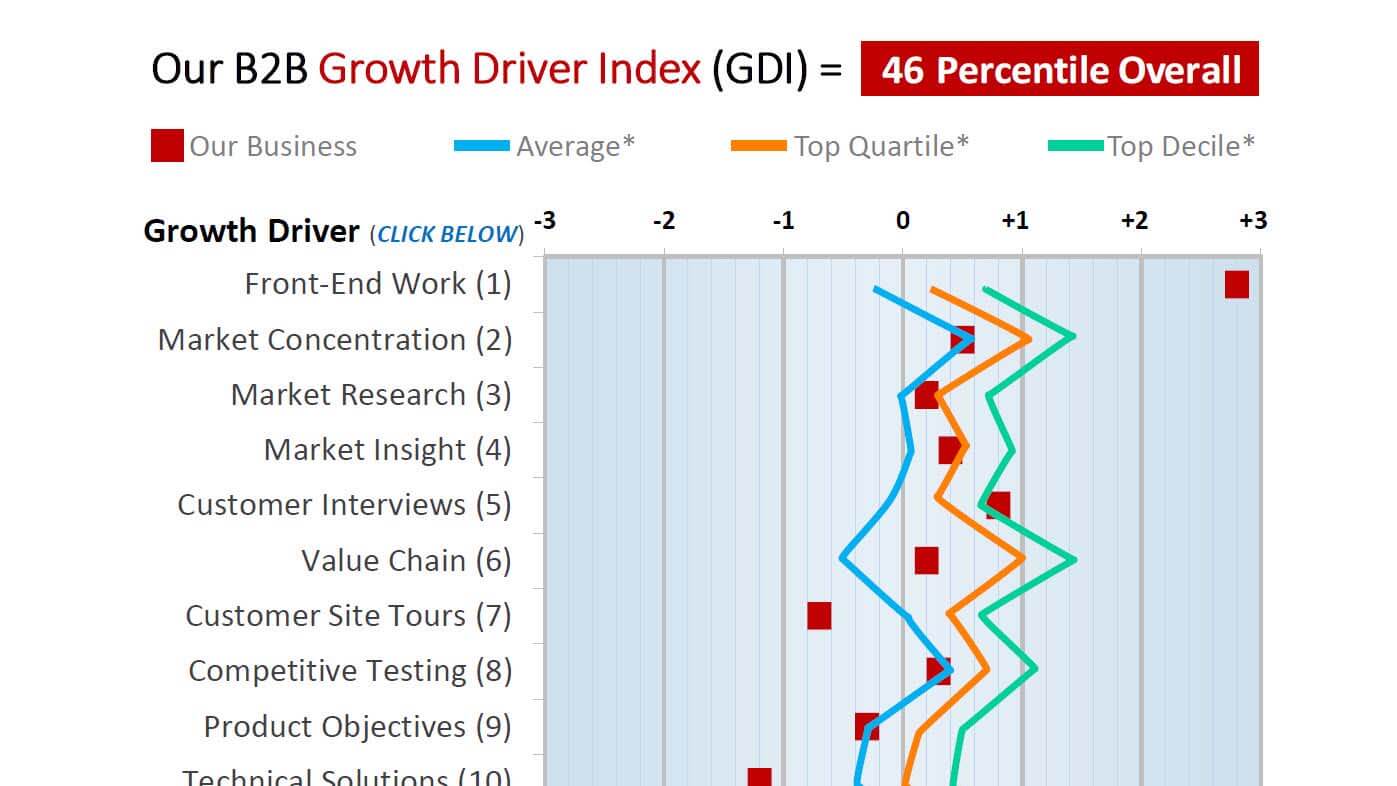
If you hired a great “business growth” coach, she’d probably have you follow the same plan as a golf or football coach: 1) objectively assess your current capabilities, 2) develop a comprehensive improvement plan, and 3) track your progress in improving these capabilities.
Why not follow this same approach for building your organic growth capabilities? Step 1 can be a free diagnostic of your business’s growth capabilities at www.b2bgrowthdiagnostic.com, which benchmarks your business against others on 24 growth drivers. You can then run this free diagnostic annually. The key word here is capabilities: Too many leaders fixate only on results, forgetting that capabilities drive results.
More in 2-minute video, Build your growth capabilities
If your company has a P/E ratio of 20, only 5% of its value comes from this year’s performance (that is, your earnings this year). The other 95% comes from the market’s expectations of your company’s future: That’s all that’s left.
So business leaders probably spend 95% of their time where the value is… ensuring future growth will be rapid, profitable and sustainable, right? Ummh… well… not so much. Strangely enough, many management teams fixate on this year’s results. You say your investors won’t let you think past this year? What about Amazon, that took 7 years to turn a profit? Warren Buffet said, “Companies obtain the shareholder constituency that they seek and deserve.”
More in this 2-minute video, Shareholder wealth is a poor goal
A builder is someone who drives business growth by delivering real value to customers, brushing aside fads, short-term distractions, and financial gymnastics. Others are remodelers, improving efficiency, quality & costs…but if nothing new is built, they lead a race to the bottom. Others are decorators, trying to boost “curb appeal,” as they focus on quarterly financials. They’re engaged in a spectator sport, not a participant sport. Finally, some are realtors, reaping their rewards during M&A… when the work of others’ hands changes hands.
Does this mean you should forget about operational efficiency, financial reporting, or M&A? Of course not. But what is your passion? For the builder, it’s delivering customer value and driving organic growth over the years.
More in this 2-minute video, Be a business builder
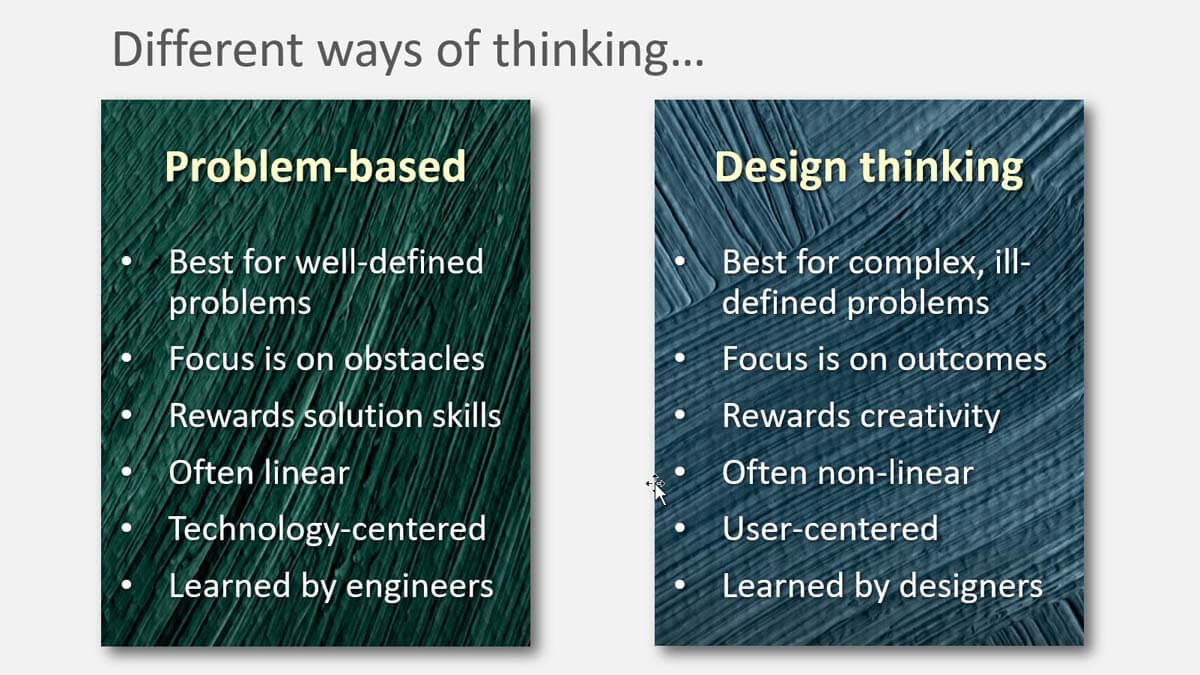
Design thinking isn’t new: The concept was first introduced by Nobel Prize laureate Herbert A. Simon in his 1969 book, The Sciences of the Artificial. It’s been “catching on” more and more in new product development circles, which is a very good thing. My favorite part is that it doesn’t start with well-defined problems, like the ones we were handed in engineering school. Rather, it’s a user-center process that encourages us to enter the customers’ world and understand it better. Especially their desired outcomes. This graphic shows the differences.
More in white paper, Design Thinking Optimized for B2B
Yes, it’s called the Commercial Confidence Index (CCI), and it’s easy to calculate: Step 1: Record your annual R&D spending for each significant product development project. Step 2: For each project, ask if you have quantified evidence of customer needs, e.g. Market Satisfaction Gaps. If “yes,” the project goes in the “Known Need” bucket. All others go in the “Assumed Need” bucket. Step 3: The CCI is your annual R&D spending on Known-Need projects divided by annual spending on all product development projects.
More in 2-minute video, Employ new growth metrics
In our white paper, B2B vs B2C: Organic growth implications for B2B professionals, we cover 12 differences between suppliers to B2B vs. consumer goods markets. Is this just an academic exercise? Not at all. Every one of these differences has implications for organic growth. The news gets better if you’re a B2B supplier: Nearly all these differences are advantages in your favor. Of course, an advantage is no advantage if you don’t take advantage of it. This white paper will show you how.
Also see the 2-minute video, Understand your B2B advantages
Here’s the test: When you look at projects in your new product pipeline, do some have sizeable commercial risk, not just technical risk? If so, you need to start conducting quantitative customer voice-of-customer interviews. These help you nearly eliminate commercial risk, based on Market Satisfaction Gaps. Here’s the point: If you’re a B2B supplier, there’s simply no reason to put up with much commercial risk once you move into the development stage. Check out over a dozen real-life examples of their use at www.aimcasestories.com.
More in white paper, Market Satisfaction Gaps
Absorb far less risk in your transformational projects by following 4 steps: 1) Diverge to many potential risk factors, 2) converge to the high-impact, low-certainty factors, 3) investigate these with a CheckPoint Plan, and 4) intelligently communicate progress to
management. ... Read More